Table of Contents
Want to know how much your money will grow over time? Whether you’re saving for a house, planning your retirement, or just curious about your investments, our future value calculator makes it super easy. Just enter your numbers, and you’ll see exactly what your savings could become in the future.
I remember when I first started investing, I had no idea how compound interest actually worked. I’d put money in my account and hope for the best. But once I used a simple calculator like this, everything clicked. Suddenly, I could see how even small monthly deposits add up over the years.
This tool helps you plan smarter. You can play around with different amounts, interest rates, and time periods to find what works best for you. No confusing math, no headaches, just clear answers in seconds.
The best part? You don’t need to be a finance expert to use it. Just fill in a few basic details about your savings or investment, and the calculator does all the work. In less than a minute, you’ll know if you’re on track to hit your money goals — or if you need to adjust your plan a bit.
What Is Future Value (FV)?
Future value (FV) represents the amount an investment will grow to after earning interest over a specific period of time. It reflects the impact of compounding, which means you earn interest not just on your original present value (PV), but also on the accumulated interest itself.
The concept is central to the time value of money, the idea that money available now is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its earning potential. A Future Value Calculator makes it easy to apply this concept in practice by showing how much your savings or investments could be worth after a number of periods, at a defined interest rate and compounding frequency.
Whether you’re making a single deposit or a series of periodic payments, using a Future Value Calculator helps in setting realistic financial goals, comparing investment options, and planning for milestones like retirement or education.
Future Value Formula
To calculate the future value (FV) of an investment, use the formula:
FV = PV × (1 + r/n)<sup>nt</sup> + PMT × [((1 + r/n)<sup>nt</sup> – 1) / (r/n)] × (1 + r/n × pmtType)
Here’s what each variable means:
- PV = Present Value (your starting amount)
- r = Annual interest rate (as a decimal, e.g., 6% = 0.06)
- n = Number of compounding periods per year
- t = Number of years
- PMT = Periodic deposit/payment
- pmtType = 0 (end of period), 1 (beginning of period)
This formula combines lump sum growth with recurring payments, taking into account both the interest rate and compounding frequency. It’s a powerful way to calculate how your investments can grow over time, whether you’re investing monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Example Future Value Calculations
Let’s see how the future value (FV) changes based on different scenarios. These examples use common inputs like present value (PV), interest rate, compounding frequency, and number of years.
Example 1: Lump Sum Investment – Annual Compounding
You invest $5,000 at an annual interest rate of 6%, compounded yearly for 10 years.
- FV = $5,000 × (1 + 0.06/1)<sup>1×10</sup> = $8,954.24
Example 2: Lump Sum – Monthly Compounding
Same amount and rate, but compounded monthly instead of yearly.
- FV = $5,000 × (1 + 0.06/12)<sup>12×10</sup> = $9,042.71
Example 3: Monthly Deposits + Interest
You deposit $200/month for 5 years, earning 4% annual interest, compounded monthly.
- PMT = $200, r = 0.04, n = 12, t = 5
- FV = $200 × [((1 + 0.04/12)<sup>60</sup> – 1) / (0.04/12)] × (1 + 0.04/12) = $13,243.39
These examples show how both compounding frequency and periodic payments (PMT) impact your final return. Even small changes in rates or intervals can significantly shift the outcome, making a future value calculator essential for planning.
How to Use the Future Value Calculator
Using this Future Value Calculator is simple. Just fill in the required fields to estimate how your money will grow with compound interest over time.
- Number of Periods (N): Enter how many years you plan to invest. For example, “10” means a 10-year term.
- Starting Amount (PV): This is your present value or initial investment. If you’re starting with $1,000, enter “1000”.
- Interest Rate (I/Y): Input the expected annual interest rate as a percentage. A rate of “6” represents 6% annually.
- Compounding Frequency: Choose how often your investment compounds, Annually, Semiannually, Quarterly, Monthly, or Daily. More frequent compounding leads to faster growth.
- Periodic Deposit (PMT): If you’re making regular deposits, enter the amount here. For example, “$100” per period.
- PMT Timing (pmtType): Choose whether payments are made at the beginning or end of each period. Most investments use “end” by default.
Once you’ve entered your values, click Calculate to get your future value (FV). You’ll instantly see how your savings grow based on the inputs and selected compounding schedule.
What Each Input Means (And Why It Matters)
Each field in the Future Value Calculator plays a key role in how your investment grows. Here’s how they work:
- Present Value (PV): This is your starting amount, the initial lump sum you’re investing. A higher present value naturally leads to a larger future value (FV) over time.
- Interest Rate (I/Y): Enter your expected annual rate of return as a percentage. Even a small change in rate can significantly affect results, especially with compounding.
- Number of Periods (N): This refers to the total number of years your money will remain invested. More periods = more time for growth.
- Compounding Frequency: Choose how often your interest is applied, Annually, Semiannually, Quarterly, Monthly, or Daily. More frequent compounding intervals amplify growth due to interest-on-interest effects.
- Periodic Deposit (PMT): This is your regular contribution per period.
Consistent PMTs build wealth steadily and speed up FV accumulation. - PMT Type: Select when payments are made, either at the beginning or end of each compounding period. Payments made earlier earn more interest, increasing your total returns.
Understanding these inputs helps you make better use of the calculator and tailor it to your financial goals.
Lump Sum vs Periodic Investments
There are two common ways to build your future value (FV): a one-time lump sum investment or a series of periodic payments (PMTs). Each approach has its strengths, depending on your financial situation and goals.
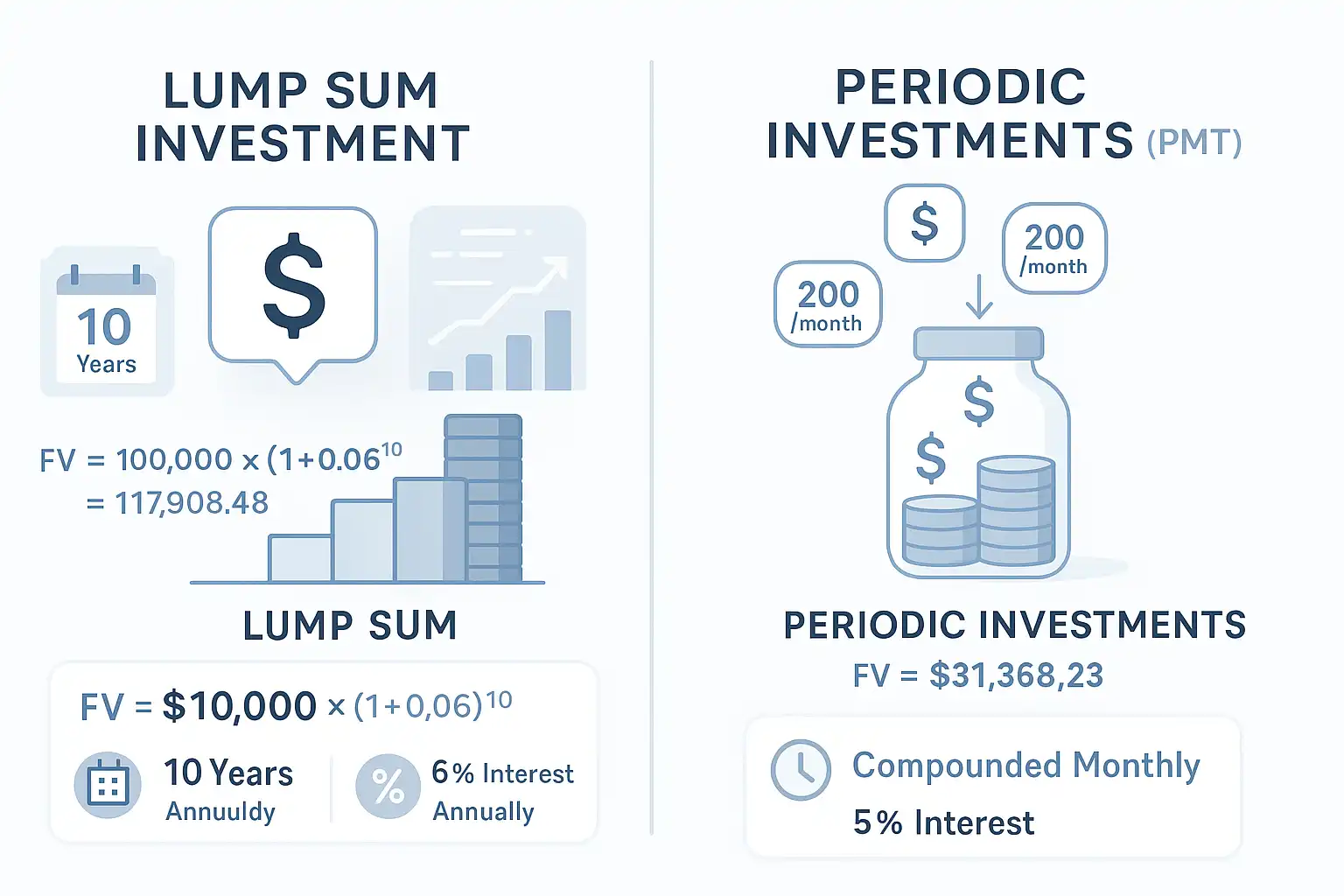
What is Lump Sum Investment
A lump sum investment means contributing a single amount up front and letting it grow over time through compound interest. This method takes full advantage of the time value of money, since every dollar is invested from day one.
Example:
You invest $10,000 at an interest rate of 6%, compounded annually, for 10 years.
- FV = $10,000 × (1 + 0.06)<sup>10</sup> = $17,908.48
The longer the money stays invested, the greater the impact of compounding. This strategy works best when you have a large amount to invest at once and want to maximize growth potential.
What is Periodic Investments (PMT)
Periodic investments involve making smaller, consistent payments over time. These PMTs could be monthly, quarterly, or yearly, depending on your compounding frequency. While each deposit has less time to grow than a lump sum, regular contributions add up and can fit better into a monthly budget.
Example:
You deposit $200/month into an account earning 5% interest, compounded monthly, for 10 years.
- FV = $200 × [((1 + 0.05/12)<sup>120</sup> – 1) / (0.05/12)] × (1 + 0.05/12) = $31,368.23
This method is ideal for budget-friendly investing, retirement contributions, or automatic savings plans. It encourages financial discipline while still benefiting from compound growth.
How Growing Annuities Work (And Why Inflation & Taxes Matter)
Growing Annuity Calculations
A growing annuity is a series of regular payments that increase at a fixed rate over time, commonly used in retirement planning or salary-based investment strategies. Unlike level annuities, which involve fixed periodic payments (PMTs), growing annuities reflect the impact of both payment growth and compound interest.
The formula for the future value (FV) of a growing annuity is:
FV = PMT × [((1 + r)<sup>n</sup> – (1 + g)<sup>n</sup>) / (r – g)]
Where:
- PMT = initial periodic payment
- r = interest rate per period
- g = growth rate of payments
- n = number of periods
Example Use Case:
You’re contributing to an investment where your annual deposits increase by 3%, starting at $2,000, over 10 years, earning 5% interest.
This method applies when you expect your income to grow and want your contributions to keep pace, common in career-linked savings, business reinvestments, or inflation-indexed retirement funds.
Growing annuities are especially powerful because they reflect both your increasing commitment and the compounding effect over time, delivering a larger future value than flat contributions.
Adjusting for Inflation and Taxes
Calculating the future value (FV) of an investment is only part of the picture, what really matters is your real purchasing power. That’s where inflation and taxes come in. Both can significantly reduce the actual value of your returns over time.
Inflation Adjustment
Inflation erodes the value of money. An investment that grows to $50,000 over 20 years might only be worth $30,000 in today’s dollars if inflation averages 2.5% per year.
To calculate real future value (adjusted for inflation), use this formula:
Real FV = Nominal FV / (1 + inflation rate)<sup>years</sup>
This helps you see what your investment will actually buy in the future, not just the inflated dollar amount.
Tax Impact
Investment earnings are often subject to capital gains tax, interest income tax, or dividend tax, depending on the account type. Failing to account for taxes can overestimate your net future value.
Some future value calculators allow you to input an after-tax return rate, giving a more realistic view. For instance, if your investment earns 7% annually but is taxed at 20%, your effective rate drops to 5.6%.
Adjusting for inflation and taxes gives you a true financial picture, helping you plan more accurately for long-term goals like retirement, education, or major purchases.
Real Future Value vs Nominal Value
When planning your financial future, it’s important to distinguish between nominal value and real future value. While both reflect your investment’s growth, only one shows its true worth in tomorrow’s dollars.
Nominal Future Value
The nominal FV is the raw result of your investment calculation, it shows how much your money will grow, not accounting for inflation or loss of purchasing power. For example, an investment might grow from $10,000 to $26,000 over 20 years at a 5% annual interest rate.
But that $26,000 won’t go as far in the future as it does today.
Real Future Value
The real FV adjusts for inflation, giving a more accurate estimate of what your investment will actually be worth in practical terms. It answers the question: “What can I buy with this money in the future?”
Formula:
Real FV = Nominal FV / (1 + inflation rate)<sup>n</sup>
For example, with 2.5% annual inflation over 20 years, that $26,000 nominal value becomes about $16,026 in real terms.
Knowing the difference helps you make smarter investment decisions, set more accurate goals, and plan effectively for long-term financial security.
Practical Applications of Future Value
Understanding future value (FV) isn’t just for math geeks, it’s a core concept behind smart financial planning. From everyday savings to strategic investments, FV helps you forecast the long-term outcome of your money decisions.
Retirement Planning
Want to know if you’re saving enough? Use Future Value (FV) to estimate how monthly contributions and compound interest will grow your 401(k) or IRA over decades. It helps answer the key question: “Will I have enough when I stop working?”
According to the CFPB’s, estimating your cumulative Social Security benefits over time, based on when you claim, your highest annual income, and average lifespan, is a key part of setting realistic retirement goals. The tool uses SSA‑based formulas to show how delaying or advancing your claim impacts both monthly and total benefits, helping you strategize accordingly.
College Savings
Parents can use FV to plan for tuition costs. With rising education expenses, knowing how a 529 plan or custodial account grows with periodic payments (PMTs) is essential for hitting future goals.
Real Estate & Business Investing
Whether you’re reinvesting profits or evaluating a property, FV shows the potential value after compounding returns. It’s also used to assess the time value of money in capital budgeting.
Emergency Funds & Short-Term Goals
Even short-term savings benefit from FV insights. Planning to buy a car in five years? FV can help set a monthly saving target, factoring in expected interest rate and compounding frequency.
In every scenario, FV makes financial forecasting clearer and decisions more grounded in math, not guesswork.
Final Thoughts
The Future Value Calculator is more than a math tool, it’s a lens into your financial future. Whether you’re investing a lump sum, making regular deposits, or planning for big life goals, understanding how compound interest, periodic payments, and time impact your money is essential.
By using future value calculations, you turn uncertainty into strategy. You gain clarity, set smarter goals, and make decisions with confidence, grounded in real numbers, not guesses.
Use this calculator often. Let it guide your path to long-term financial growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Got questions? Our FAQs cover common topics about how our tools work, tips for accurate calculations, and guidance on using InterCalculator for everyday money decisions.
What is a Future Value Calculator used for?
A Future Value Calculator helps you estimate how much an investment or savings will be worth at a future date. It considers factors like principal amount, interest rate, time period, and compounding.
Why is future value important in financial planning?
Knowing the future value of money helps you set realistic financial goals. It shows how today’s savings and investments can grow over time, making it easier to plan for retirement, education, or large purchases.
Does the calculator account for inflation?
Most basic calculators do not automatically adjust for inflation. However, you can factor it in manually by lowering the expected interest rate to get a more realistic estimate.
Can I use the Future Value Calculator for both savings and investments?
Yes. It works for both savings and investments by estimating how money grows over time using an interest or return rate.
Why is the final savings less than expected with multiple discounts?
Each discount is applied to a reduced amount, not the original price, so the total savings are less than simply adding the percentages.
This calculator was created by the InterCalculator Editorial Team, led by Haris Farooq (Formula & Development). Our team specializes in formula research, calculator logic, and technical development, ensuring each tool is accurate, fast, and easy to use.
View Editorial Team →Before publishing, every calculator goes through the InterCalculator Accuracy Review Process. For the Future Value Calculator, we verify formulas against trusted financial standards for compound interest and growth projections. We test results across multiple deposit amounts, interest rates, and time scenarios to ensure accurate and consistent outcomes. All calculations are reviewed with an experienced finance expert to confirm accuracy, clarity, and reliability.
View Process →